In the modern world, capacitive and resistive touch screens have become an integral part of our daily lives, from smartphones and tablets to ATMs and interactive kiosks. These intuitive interfaces allow users to interact directly with electronic devices, making them more user-friendly and accessible. Among the various touchscreen technologies available, two prominent contenders are capacitive and resistive touchscreens. While both serve the same purpose, they operate on different principles and offer distinct advantages. In this article, we will delve into the differences between capacitive and resistive touchscreens to help you understand their unique characteristics.
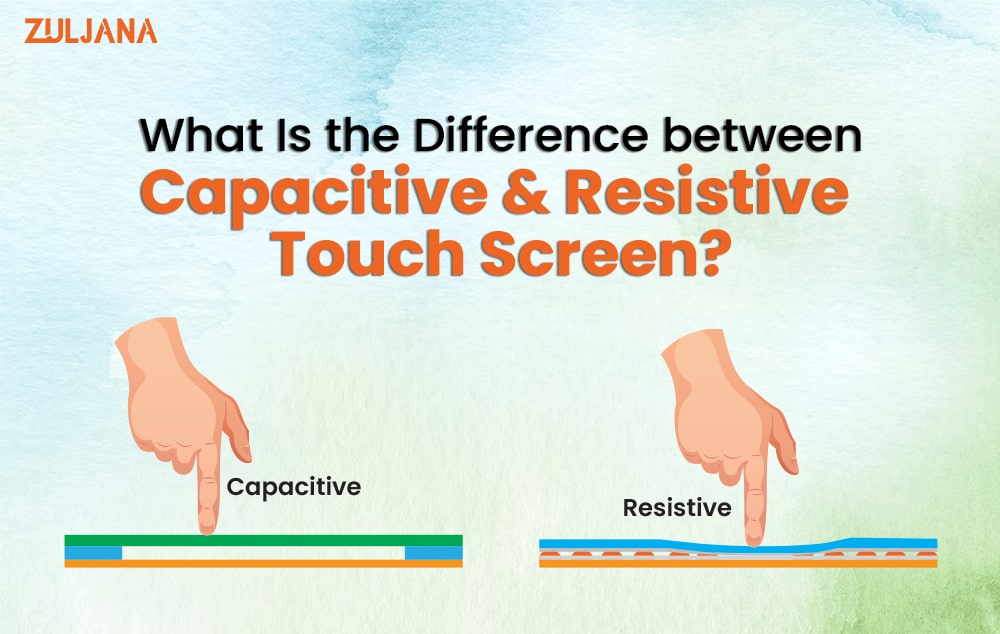
Difference Between a Capacitive and Resistive Touch Screen
1. Principle of Operation:
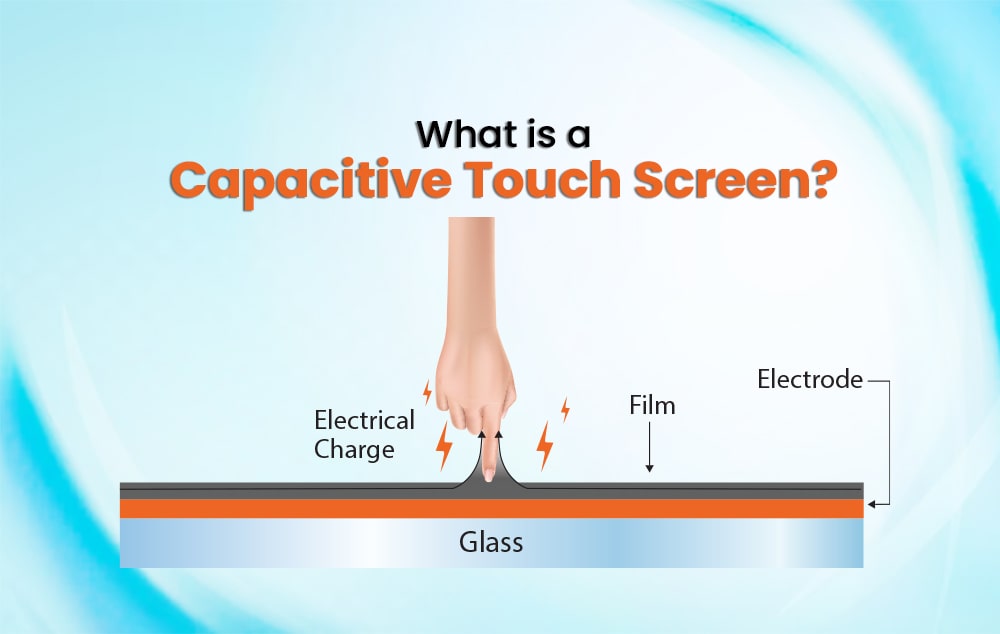
Capacitive Touchscreen:
Capacitive touchscreens work based on the principle of capacitance, which measures the electrical charge stored in a conductive material. They consist of multiple layers, with the top layer being a glass or plastic panel coated with a transparent conductive material, often indium tin oxide (ITO). When you touch the screen with your finger (which acts as a conductor), it creates a disturbance in the screen’s electrostatic field. This change in capacitance is detected by the touchscreen controller, which then processes the touch input.
Resistive Touchscreen:
Resistive touchscreens, on the other hand, utilize a different approach. They comprise multiple layers as well, typically two flexible sheets coated with a resistive material and separated by small air gaps. When pressure is applied to the screen, the top layer makes contact with the bottom layer at the specific point of touch. The touch is then detected based on the change in electrical resistance between the two layers at the point of contact. A controller interprets this resistance change and converts it into a corresponding touch input.
2. Touch Sensitivity:
Capacitive Touchscreen:
Capacitive touchscreens are highly sensitive and provide a more responsive and smooth touch experience. They can detect multiple touch points simultaneously, enabling gestures like pinch-to-zoom and multi-finger gestures. Capacitive screens respond to the slightest touch, making them ideal for tasks that require precision and speed.
Resistive Touchscreen:
Resistive touchscreens are generally less sensitive than capacitive screens. They require a firmer touch or pressure to register the input, which can sometimes result in slight inaccuracies during touch recognition. The lack of multi-touch support limits their ability to perform certain gestures, making them less suitable for modern, gesture-driven applications.
3. Durability and Sturdiness:
Capacitive Touchscreen:
Capacitive touchscreens are known for their durability and robustness. The top layer, often made of tempered glass, provides excellent protection against scratches and impact. However, they are more susceptible to damage from sharp objects or excessive force applied to the screen.
Resistive Touchscreen:
Resistive touchscreens tend to be more durable than capacitive ones due to their construction. The multiple layers and flexible nature of the screen allow it to withstand a greater amount of pressure. They are less prone to damage from rough handling and are suitable for environments where the screen might be subjected to more abuse.
4. Clarity and Transparency:
Capacitive Touchscreen:
Capacitive touchscreens offer exceptional clarity and transparency since they use a single layer of glass or plastic as the top surface. This results in a bright and vibrant display with better light transmission, allowing for a more vivid visual experience.
Resistive Touchscreen:
Resistive touchscreens can be slightly less transparent than capacitive ones because of the multiple layers and air gaps. The additional layers might cause a slight reduction in display clarity and brightness. However, advancements in technology have minimized this difference to a considerable extent.
5. Use of Stylus:
Capacitive Touchscreen:
Capacitive touchscreens generally do not respond to regular styluses, as they require an electrically conductive touch. However, there are special capacitive styluses available with a conductive tip that allows users to draw or take notes on the screen.
Resistive Touchscreen:
Resistive touchscreens are compatible with regular styluses, including those made of plastic or other non-conductive materials. The pressure-based touch detection makes it easier to use a stylus for precise input.
6. Cost and Applications:
Capacitive Touchscreen:
Capacitive touchscreens are more expensive to manufacture due to the complexity of the technology and the high-quality materials used, such as tempered glass. They are commonly found in high-end smartphones, tablets, and premium electronic devices.
Resistive Touchscreen:
Resistive touchscreens are relatively more affordable to produce, making them suitable for a wide range of applications. They are often used in budget smartphones, GPS devices, industrial equipment, and some older devices where multi-touch and high sensitivity are not critical requirements.
Conclusion:
Both capacitive and resistive touch screens have their distinct advantages and applications. Capacitive touchscreens offer a more responsive and intuitive experience with multi-touch support, making them ideal for modern smartphones and tablets. On the other hand, resistive touchscreens are durable and cost-effective, making them suitable for industrial and budget-friendly devices.
When choosing between the two, consider your specific requirements, the level of touch sensitivity needed, and the device’s intended use. Understanding the differences will help you make an informed decision and ensure a satisfying user experience with your chosen touchscreen technology.